We are providing here the highlights and short summary about the Census conducted by the Office of the Registrar General and Census Commissioner, India, in Ministry of Home Affairs which was published on March 31.
- This is the 15th Census of India and the 7th Census of Independent India-2011 was started on 1st April 2010 with President Smt.Pratibha Patil being the first citizen to be accounted.
- The cost of the Census was estimated to be 22 Billion Rupees.
- The motto of Census 2011 – ‘Our Census, Our future’.
- The logo of Census has been explained in the image below.

- The census of India is organised every 10 years, hence called decennial. It is the primary source of information about the demographic characteristics of the population of India.
- The 2011 census was the largest census conducted in the history of mankind.
- The first Census in India took place in 1872. But first regular census was initiated in 1881 by Lord Rippon.
- This 2011 Census commenced on 1 May 2010 with a mandate to create a National Population Register including photographs and fingerprints of every resident of the country(not citizens but residents).
- As mentioned earlier, the census is conducted by the office of the Registrar General and the Census Commissioner of India,which is an office in the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, under the provisions of Census of India Act, 1948.
- The Census of India Act, 1948 gives Central Government powers to notify a date for Census; power to ask for the services of any citizen for census work. The law also makes it compulsory for every citizen of country to answer the questions as part of census, truthfully and honestly. The Act has provisions for penalties to punish false answers or not giving answers to the census questionnaire.
- One important provision of this act is the guarantee for the maintenance of secrecy of the information collected during the census. It is to be noted that the census records are not to be inspected and also they are not admissible as evidence.
- The population of India has seen an increase of more than 181 million during the last decade 2001-2011.
- The percentage growth during 2001-2011 is 17.64%. The male population rose by 17.19% and females by 18.12%.
- Note: The 2001-2011 decade is the first decade (the exception of 1911-1921 remains, they being war years) which has added lesser population in comparison to the previous decade population addition.
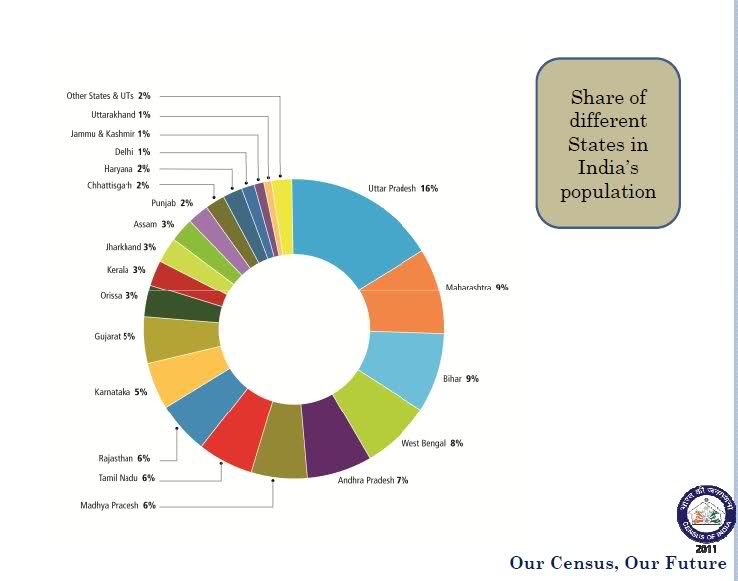
- Uttar Pradesh with a population of 199.5 million is the most populous State in India, followed by Maharashtra with 112 million people.
- The Child Population in the age group of 0-6 years is 13.1% of the total population, while the corresponding figure for 2001 census was 15.9%. There was a decline of 2.8 percent points over a decade.
- <<<<<<<<<<Read more in General Awareness here>>>>>>>>>>>>
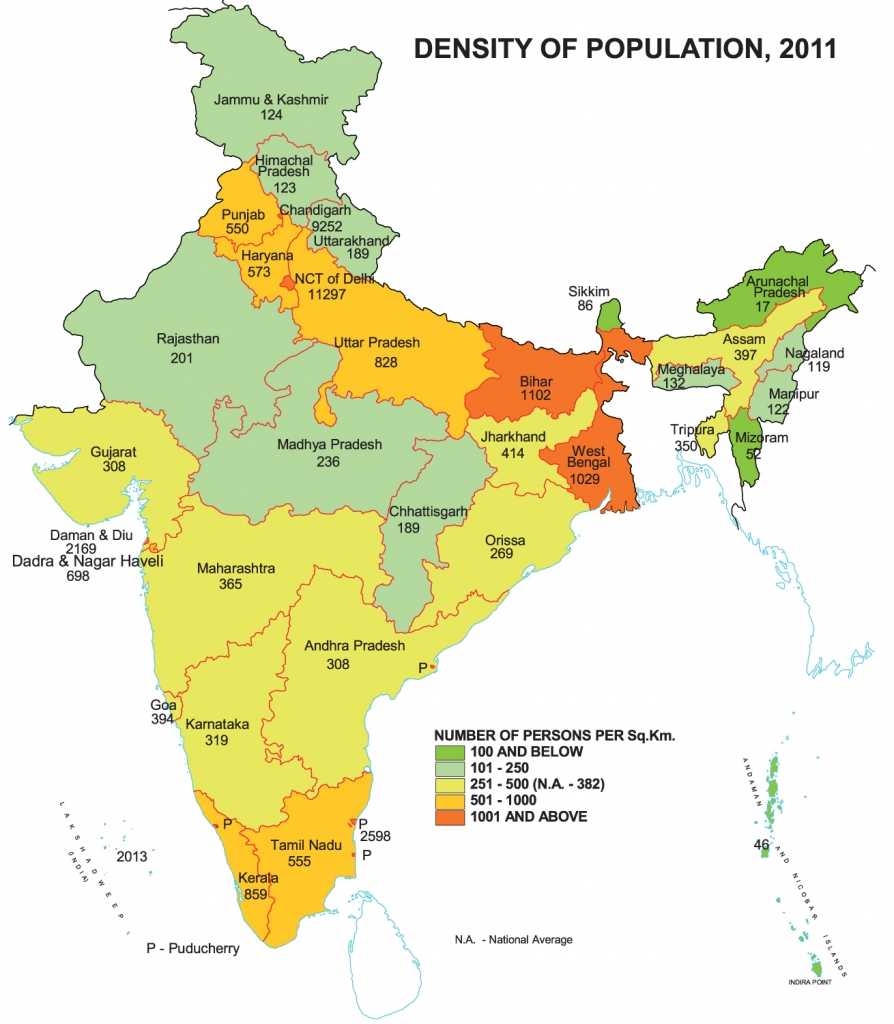
- The overall sex ratio at the national level has seen an increase of 7 points to attain 940 in Census 2011 as against 933 in Census 2001 data. In fact, this is the highest sex ratio in records since the Census of 1971. The increase in sex ratio is observed all over but three major States – J&K, Bihar and Gujarat have recorded a decline in sex ratio in comparison to the Census 2001 data.
- Kerala recorded a sex ratio of 1084, that is the highest sex ratio in country. It is closely followed by Puducherry with 1038. Opposed to these, Daman & Diu has recorded the lowest sex ratio of 618 in the census 2011.
- The total number of children recorded in the age-group of 0-6 is 158.8 million (a decrease of 5 million since census 2001).
- Therefore, 20 States and Union Territories now have over one million children in the age group of 0-6 years. On the other end, there are 5 States and Union Territories which are yet to reach the one million mark.
- It should be noted that Uttar Pradesh has 29.7 million children, Bihar has 18.6 million, Maharashtra has 12.8 million, Madhya Pradesh has 10.5 million and Rajasthan has 10.5 million children in 0-6 years of age. These states constitute 52% children in the age group of 0-6 years in the country.
- Population of children beloging to 0-6 years age in the decade of 2001-2011 has registered a decline of 3.08 % growth.
- The child sex ratio for 0-6 years age is 914. There is an increasing trend in the child sex ratio (0-6years) in states of Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Mizoram and A&N Islands. In all other remaining 27 States and UTs, the child sex ratio has showed a decline in comparison to the Census 2001.
- It should be noted that, Mizoram has the highest child sex ratio in 0-6 years of age with 971 female children per 1000 males. It is closely followed by Meghalaya with 970 female child. On the contaray, Haryana is at the bottom of the list with a depressing ratio of 830 females per 1000 males, followed closely by Punjab with 846 females.
- Literacy rate of the country has gone up from 64.83% in census 2001 to a 9.21 point increse to reach 74.04% in census 2011 showing progress.
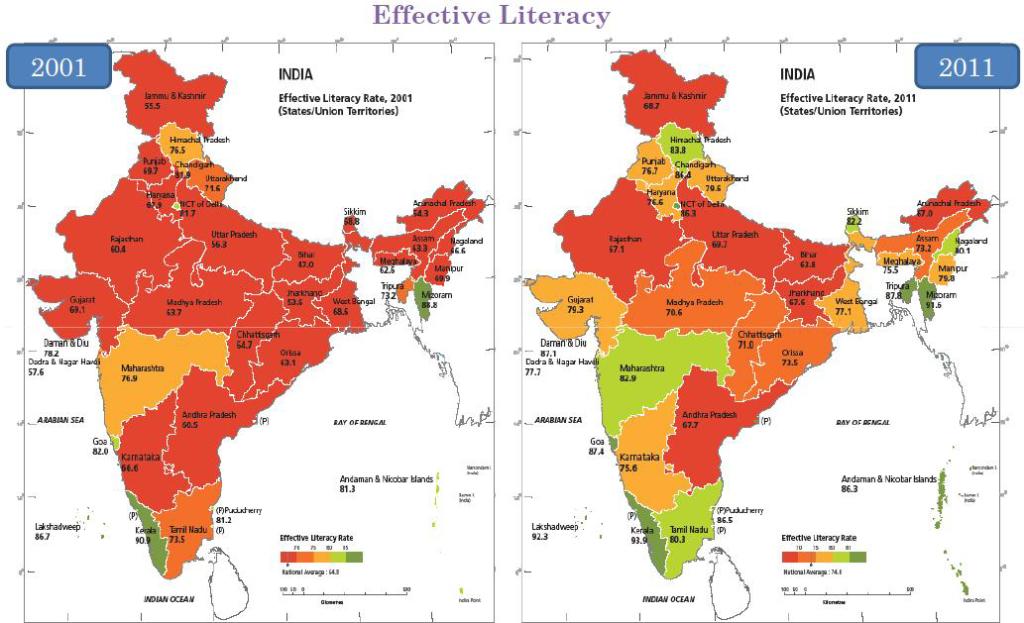
- Gender wise percentage growth in literacy during 2001-2011 decade is 38.82%. For males it increased by 31.98% and for females the literacy rates increased by 49.10%.
- Literate population now constitutes 74 % of the total population in age group 7 and above, while illiterates constitute 26 per cent of the population in the census 2011 data.
You can bookmark this page for future reference and revision. Questions based on census data are asked in various competitive exams including bank exams. These highlights of census 2011 will serve the purpose to initiate you into going into details of the census data. Thereafter you can look and understand the summary of census as well for higher and in-depth data.





