We are presenting here gems selected from the Economic Survey 2013-14, about the Indian industries and their role in Indian economy. Therefore, the fellow students can be sure that the data given below is latest and comes from government sources. We hope that this compilation for Economics Study Material & Notes will be particulaly useful for civil services mains paper IV exam.

Before we begin, a brief about the Indian industry scene. Broadly, there are three major industrial economic sectors in India.
- The primary sector, which mainly extracts raw material. Such as mining and farming industries.
- The secondary sector, involves refining, construction, and manufacturing.
- The tertiary sector is concerned with services and distribution of manufactured goods.
<<<<<< Read about role of Agriculture in Indian Economy based on economic survey>>>>>>>
Indian Industrial sector, hence, consists of manufacturing, mining, electricity, and construction. After the economic crisis in 2008, it showed considerable recovery and steady growth for three years but then lost the track after that. This was due to constraints on both supply-side and demand-side. Therefore, Industrial performance in 2013-14 has maintained its lackluster growth for the second successive year.
- The latest GDP estimates depict that industry grew by 0.4 per cent in 2013-14 after being 1% in the year 2012-13.The projected 12th Five Year Plan target is 10 per cent growth rate for the manufacturing sector and 5.7 per cent for the mining sector in the remaining three years.[/box]
- A sector-wise analysis of the industrial performance depicts that the main reason for low performance is- contraction in mining activities and reduced manufacturing output.
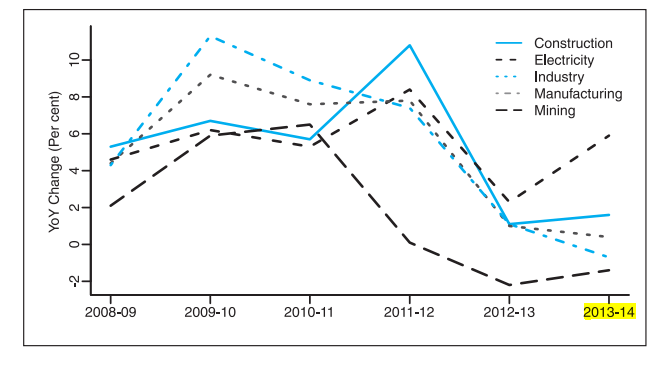
A sector-wise analysis of the industrial performance over the years in Indian Economy
- <<<<<<<<<More about Price Indexes including IIP here>>>>>>>>>
- The industrial sector showed a growth of 0.4 percent in 2013-14. This poor performance is attributed to the contraction in mining and slowdown in manufacturing.
- Manufacturing and mining-sector GDP has declined due to reduction in investment especially by the private corporate sector during last three years.
- Natural gas production has declined primarily due to declining level of production from the KG-6 basin. But electricity generation has increased in comparison to the previous year by 2.1%, due to significant capacity addition in the recent years.
- The steel and cement sectors show capacity underutilization due to slowdown in construction sector.
- The “core” industries witnessed a declined from 6.5 per cent growth during 2012-13, to 2.7% during in 2013-14. This is because of decline in natural gas and crude oil production, and reduced growth in fertilizers, coal and refinery products.
S.no. Core industries : 1. Natural gas 2. Fertilizer 3. Coal 4. Electricity 5. Crude oil 6. Refinery products 7. Steel 8. Cement
- The total foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows into services, construction, drugs and pharmaceuticals, automobile industry, metallurgical industries, telecommunications, computer software and hardware, power, and hotels and tourism sectors have increased by 22.8% in 2013-14.
- Growth of credit flow to the industrial sector was lower in 2013-14 as compared to the past year.
- Cheering Positives: There is remarkable growth in textiles, electrical equipment and electricity generation even after capacity underutilization due to fuel supply bottlenecks.
Environment and industry Linkages:
- Environmental degradation is largely a result of market failure, because there is a non-existent or poorly functioning market for environmental goods and services. One reason for market failure is the lack of well-defined property rights.
- Environmental degradation is therefore a case of consumption/production externalities showed by the divergence between private
as well as social costs or benefits. - Market distortions that are created by price controls and subsidies aggravate the attainment of environmental objectives.
- The natural resource depletion in terms of fossil fuel, minerals, timber, water, air, as well as coastal,marine, and land contamination, and loss of biodiversity show that there is a heavy load on the environment.
- This is particularly through intensive resource and energy use in industrial energy (fossil fuel) and in major air-polluting industries (petroleum refining, fertilizers, and cement, iron and steel, other metallic and non-metallic minerals extraction) have contributed to a great deal in air and water pollution.
- Waste management problem: Large quantities of industrial and hazardous wastes from expansion of chemical-based industry causes serious health hazards.
<<<<<<<Click here to Read about Economic Planning in India>>>>>>
Challenges for industrial sector:
- Revival of Business Sentiment in order to boost Investment by the Corporate Sector
- Removal of Infrastructure Bottlenecks: For improving infrastructure there is a need to alter coal production by permitting commercial coal mining. Also a restructuring of power distribution, upgradation of road and rail networks, reduction in delays for regulatory approvals, land acquisition and rehabilitation, require urgent attention. Projects need to be considered under public-private partnership (PPP) mode to attract private-sector investment in infrastructure.
- Facilitating Growth of Small Businesses: The informal sector lacks easy access to credit and technology while it a major contributor in GDP. Also, India’s ‘Ease of Doing Business’ ranking by the World Bank has been reduced from 131 to 134 out of the 189 countries in
2014. This needs to be corrected by building a consensus among the States on best practices to be applicable to all the states and also to promote self-certification, e-returns, and e-filings to make business environment friendly for entrepreneurs and corporates as well. - There is a need to promote structural changes in Manufacturing industries in medium term for Indian economy : The medium-term challenge for Indian manufacturing is to progress from lower to higher technology consuming sectors; from lower to higher value-added- sectors; and from lower to higher productivity sectors.
These snippets from the economic survey will be useful for the Essay paper also. We will keep updating the data as new statistics release. You can bookmark the page for future reference. More articles will be added to the Economics study material & notes section.





