The Imperial Chola Dynasty Empire
After Sangam, the Chola became feaudatories of Uraiyur . These later Cholas are termed as “Imperial Cholas” because they excercised ocntrol over Sri Lanka and Malay Peninsula. thousands of inscriptions in temples tell about their administration, society, economy and culture.
Muttaraiyar family in Kaveri delta, were subordinate to the Pallava kings of Kanchipuram. Vijayalaya Chola belonging to Uraiyur captured the kaveri delta from Muttaraiyar in mid 9th century. Vijayalaya built Thanjavur town with temple for Goddess ‘Nishumbhsudhini'(Goddess Durga).
His son Aditya defeated the Pallava king Aparajita and annexed Tondaimandalam. He was succeeded by Parantaka I, who defeated Pandayas and the ceylonese ruler. But he lost the Battle of Tokkolam with Rashtrakutas. Parantaka I built temples, provided golden roof on Vimana of Nataraja temple at Chidambaram. The Uttarmerur inscription describing village administration under Cholas belong to his reign.
After 30 years of Parantaka I, Rajaraja I usurped the throne for duration of 985 AD to 1014 AD. He defeated Chera and Pandayan rulers, extending his empire upto river Tungabhadra. He led naval expedition against Maldives and captured it. Rajaraja I held titles like: Mummidi Chola, Jayankonda, Sivapadasekara. He was a follower of Shaivism, hence built temple for Shiva, Rajrajeshwara temple popularly known as Bhrihadeshwara temple at Thanjavur in 1010 AD. This temple is part of UNESCO World Heritage Site in India under ” Great living Chola Temples”. He also patronized a Buddhist monastery at Nagapattinam.
Rajendra I succeeded his father in 1014-1044 AD. The 1000th Year of his Coronation completed in 2014. He defeated the ceylonese king Mahinda V and conquered the whole Sri Lanka including the northern and Southern parts. He also defeated Jayasimha II of western Chalukyas and marked Tungabhadra was marked boundary between Cholas and Chalukyas. Rajendra I crossed the Ganges and conquered many on his way to strengthen the Chola empire. 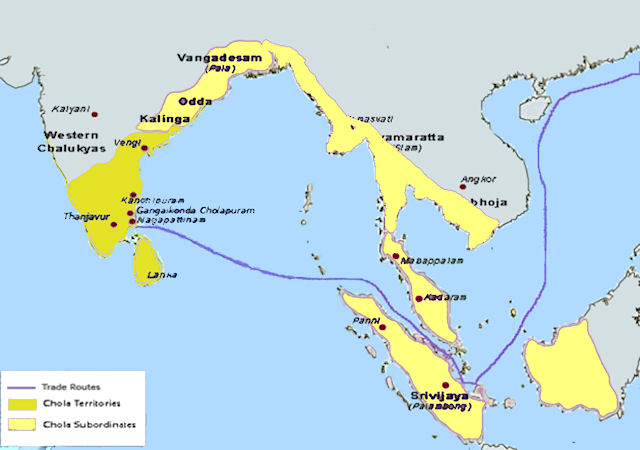 To commorate this feat, he constructed and founded Gangaikondacholapuram. He also summoned excavation of a large irrigation tank at Cholagangam. He also sent Naval expedition to Kadaram or Sri Vijaya(Malay Archipelago) to confront them for stopping Chola trade with China. Chola Empire achieved its peak under Rajendra I. He assumed titles like, Mudikondan, Gangaikondan, KadaramKondan, PanditaCholan. Rajendra I was a Shivite and gave huge endowments to Lord Nataraja temple at Chidambaram. He was tolerant to Vaishnaism and Buddhism.
To commorate this feat, he constructed and founded Gangaikondacholapuram. He also summoned excavation of a large irrigation tank at Cholagangam. He also sent Naval expedition to Kadaram or Sri Vijaya(Malay Archipelago) to confront them for stopping Chola trade with China. Chola Empire achieved its peak under Rajendra I. He assumed titles like, Mudikondan, Gangaikondan, KadaramKondan, PanditaCholan. Rajendra I was a Shivite and gave huge endowments to Lord Nataraja temple at Chidambaram. He was tolerant to Vaishnaism and Buddhism.
After Kulottunga I and kulottunga II, Rajendra III was last chola who defeated Pandayan King Jatavarman Sundarapandaya II.
Chola Art and Architecture :
The Dravida style of architecture reached its zenith during the Chola empire. The main feature of Chola style of Architecture is a building of five to seven storeys in a typical style known as “Vimana” above the chief pillared hall with flat roof was placed in front of the sanctum known as “mandap”.  This mandap functioned as an audience hall and a place for various ceremonies. Sometimes, a passage was also constructed around the sanctum to enable devotees to walk around it, where many images of other Gods were placed. This passage was then enclosed with high walls and large gateways known as “Gopurams”.
This mandap functioned as an audience hall and a place for various ceremonies. Sometimes, a passage was also constructed around the sanctum to enable devotees to walk around it, where many images of other Gods were placed. This passage was then enclosed with high walls and large gateways known as “Gopurams”.
The Brihadeshwara temple/ Rajrajeshwara Temple at Tanjore is classic example of Dravida style of architecture under Chola empire. Gangai-kondan Cholapuram temple is another such example.
<< Read about headquarters of important international organisations here>>
Cholan craftsmenship extended beyond temple architecture to include Bronze image making.  The bronze statue of Nataraja is an example of great skills attained during Cholan period. The bronze statues under the chola empire were created by the ‘lost wax technique’, which allowed the inclusion of various intricate features.
The bronze statue of Nataraja is an example of great skills attained during Cholan period. The bronze statues under the chola empire were created by the ‘lost wax technique’, which allowed the inclusion of various intricate features.