Difference between Hinayana And Mahayana Buddhism – History Study Material & Notes
For many centuries after Buddha’s demise, Buddhism strived in its earlier form. But by the advent of 1st century AD, anew doctrine emerged which was different and distinct in ideas and practices from the previous orthodox Buddhism.
These schools have been divided into the two Yanas or ‘Vehicles’ or ‘Paths’. These two are: the Hinayana and Mahayana. A ‘Yana’ is referred to the vehicle that one takes to reach from the sufferings to enlightenment. In layman’s terms, a Hinayana is a lesser vehicle while Mahayana is a Greater vehicle.
Hinayana:
- Early Buddhist teachings gave more importance to self-realization and effort in achieving nirvana.

- the ideal of Hinayana is individual salvation, thus it is considered lesser vehicle.
- The Hinayana or Theravada doctrine believes in the original teaching of Buddha, or the old, respected path of theras.
- They doesn’t believe in Idol Worship.
- Hinayana teaches that, to attain individual salvation the path goes through self discipline and meditation.
- It should be noted here that Asoka patronized Hinayana
- Pali, the language of masses was used by the Hinayana scholars.
- It is also called the “Deficient Vehicle”, the “Abandoned Vehicle”, Stharvivada or Theravada meaning “doctrine of elders”.
- Hinayana stresses on righteous action and law of karma.
- The Hinayana ideal is Arhat, the one who strives for his own redemption.
- Hinayana regards Buddha as a man, of extraordinary knowledge, but just a man, therefore, do not worship him.
- It is developed around the acts of Buddha.
- Hinayana believes in salvation by works, that each man should work for his own salvation.
- Hinayana scriptures are written in Pali, and founded on the Tripitakas.
- Hinayana or Theraveda traditions are followed in SriLanka, Laos, Cambodia, other South-east Asian countries.
Mahayana:
- Mahayana believes firmly in the spirit of Buddha’s teachings.
- Mahayana scriptures are written in form of Sutras in Sanskrit.
- This form of Buddhism gained recognition at the time of Kanishka. The Third Buddhist Council recognised these two forms of Buddhism.
- It believes in salvation by faith.
- Mahayana is developed around the symbolism of Buddha’s life and personality.
- The Mahayana ieal is salvation for all, that is why it is called as greater vehicle.
- Mahayana holds the law of karuna / compassion over and above the law of karma.
- Mahayana upholds the ideals of Boddhisatva / the saviour – who is concerned about the salvation of others.
- This sect believes in the divine qualities of Buddha and thus believes in Idol Worship.
- It is also known as the Bodhisattva Vehicle.
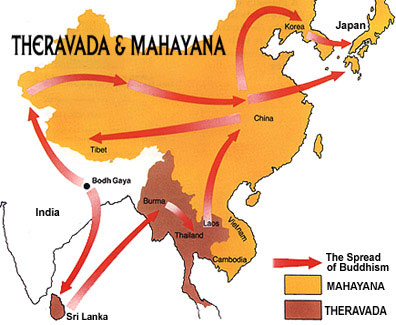
- Mahayana Buddhism is spread across India, China, Japan, Vietnam, Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, Nepal, Tibet, Bhutan, and Mongolia. Tibetan Buddhism is a traditions of Mahayana only.
- The fundamental principles of Mahayana doctrine are based on the possibility of universal liberation from suffering for all beings. Therefore this is considered the “Great Vehicle”.
- The doctrine of Bhakti has evolved as a characteristic feature of Mahayana Buddhism.
- “Nagarjuna” was the most outstanding exponent of Mahayana Buddhism.
<< Read about Inflation here >>