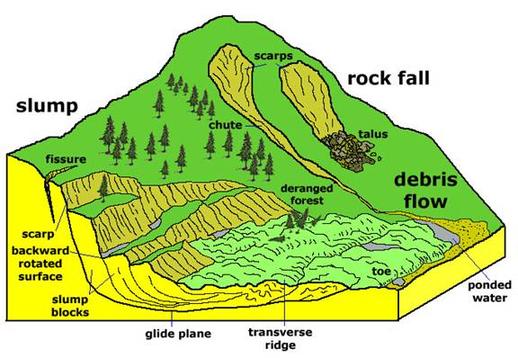
In India, the Himalayas are prone to landslides, particularly n monsoon season, from months of June to October. Various types of landslides occur in Himalayas, including block slumping, debris flow, debris slide, rock fall, rotational slip and slump.
What is a landslide?
A landslide is the gravitational movement of a mass of rock, or mass of earth or debris, downwards on a slope. It generally occurs when a hilly slope becomes unstable due to natural reasons such as groundwater pressure acting to destabilize the slope, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, erosion, etc.
Which human activities influence landslides in India?
Landslides are induced by human activities such as deforestation, dynamite blasting of rocks, earth work, constructions, vibrations from big machines, etc. The activities that require cutting down of trees are mainly considered to induce landslide in prone areas. The trees work through their roots that hold the soil in place.
Effects of Landslides in India?
Generally landslides are triggered by heavy or prolonged rainfall. Landslides cause severe damage to lives and property while also causing disruption in communication networks and movement of traffic.
- Every year, landslides in the Himalayan region kill people and cause damage to several villages leaving them unfit for habitation.
- Landslides create blockades in the road network and also in river system, which causes flood.
- The terraced farm fields that are destroyed by landslides, cannot be easily recovered or made productive again.
- Affected by landslides, the road network remains closed for long periods, hence, causing huge hardships to people inhabiting and dependent on the area for their basic supplies and provisions.
- Landslides disrupt water sources and chocked them by debris fall.
- Due to landslides, the river sediment load is increased considerably, which results in irregular courses of river and frequent breaching of banks also resulting in unexpected floods.
- The water channels are also affected due to disruption in previous channels, this leads to disturbance in water supply to dependent villagers for irrigation purposes. This then adversely affects agriculture production in the affected region.
Causes of Landslides in India – Reasons
Landslides in India are considered a major hazard in most hilly and mountains regions as well as in steep river banks and coastlines. The causes of landslides in India are not much different from the world, but there are some peculiarities. Important factors considered to be responsible for causing landslides are:
- Slope instability due to removal of lateral and underlying support.
- Indiscriminate chopping down of trees.
- Slash and burn cultivation practices in hills
- Road construction and mining activities.
- With increasing population pressure, there is an increase in grazing activities, urbanization which reduces dense natural evergreen forest cover.
- Due to these activities the ecological balance is disrupted, thereby resulting in loosening of the soil.
- Under conditions of heavy rain, there is increased and substantial soil erosion and frequent landslides.
Landslide Hazard Zonation map of India:
The major areas affected by landslides in India are divided mainly in following regions as landslide-prone areas in India. These are based on landslide hazard zonation:
- The Western Himalayas (in states of Uttar Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir)
- The Eastern & North-eastern Himalayas (in states of West Bengal, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh)
- The Naga-Arakkan Mountain belt (in states of Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura)
- The Western Ghats region including Nilgiris (in states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala & Tamil Nadu)
- The Plateau margins of the Peninsular India and Meghalaya plateau in North-east India.
The following map of landslide prone areas in India will be useful in remembering the areas mentioned above.
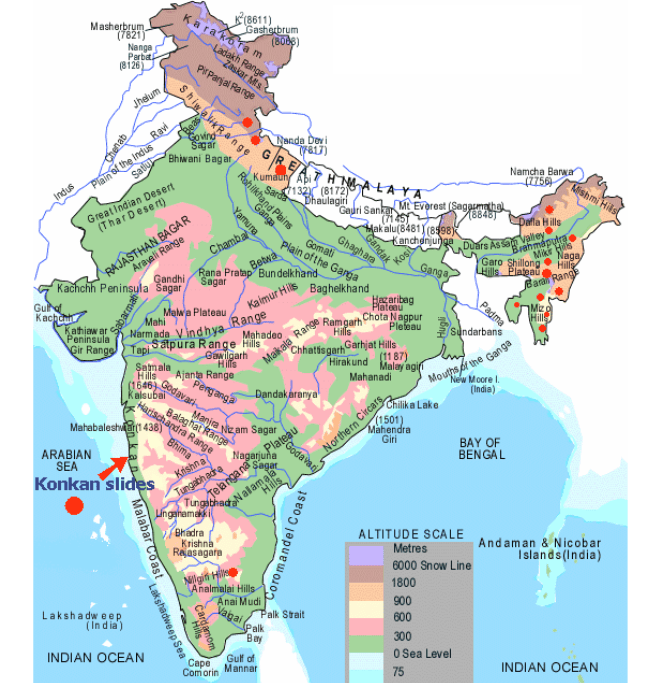
Areas prone to landslides in India on map
The Nodal agency responsible for early warning of landslide disaster in India is – Geological Survey of India.
Mitigation Steps for landslides in India
- Excess water in catchments areas should be stored to reduce the effect of flash floods, this will also recharge the ground water level in areas prone to landslide in India.
- The runoff collection ponds in the catchment areas must be dug to store water.
- On community lands, fuel or fodder trees should be grown to increase forest cover to reduce landslide hazard in India.
- Grazing should be restricted and better grass must be grown on the surface previously grazed to increase the hold on soil by plant roots. These grasses can be of some commercial importance so that economic returns encourage farmers in areas prone to landslide in India.