98% of Earth’s crust is made up of 8 elements, namely: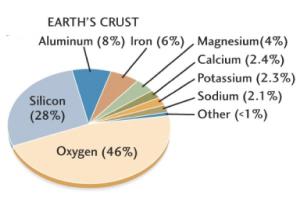
- Oxygen
- Silicon
- Aluminium
- Iron
- Calcium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Magnesium
And rest is constituted by titanium, hydrogen, phosphorus, manganese, sulphur, carbon, nickel and other elements.
Elelments combine with each other to form minerals. Mineral is a naturally occurring organic and inorganic substance, which is composed of two or more elements.
Basic source of all minerals is hot magma in interior of Earth.Physical characterstics:
- External crystal form : It is determined by internal arrangement of the molecules. It can be in shape of Cubes, octahedrons, hexagonal prisms, and others.
- Cleavage : tendency to break in given directions producing relatively plane surfaces.
- Fracture : The internam arrangement so complex there are no planes of molecules, the crystal will break in an irregular manner.
- Lusture: appearance of a material without regard to colour. Each mineral has a distinctive lusture like mettalic, silky, glossy, etc.
- Colour: Some minerals have characterstic colour determined by their molecular structure – malachite, azurite, etc. Some minerals are coloured by impurities, example, quartz may be white, green, red or yellow based on impurities.
- Streak : Colour of the ground powder of any mineral is known as streak. May be same colour as mineral or may differ- malachite is green and gives green streak but flourite is purple or green and gives a white streak.
- Transparency : Light rays pass through so that objects can be seen in plainly; Translucent – light rays pass through but will get diffused so that objects cannot be seen clearly through it; Opaque: light rays will not pass through.
- Structure: Particular arrangement of individual crystals, fine , medium, or coarse grained; fibrous- separable, divergent, radiating.
- Hardness : Related resistance on being scratched; Ten minerals are selected to measure the degree of hardness from 1 to 10 on Mohs scale.

- Specific gravity: Ratio between the weight of a given object and the weight of an equal volume of water. Then the object weighed in air and weighed in water, and further divide weight in air by the difference of the two weights.
Major minerals with their characteristics:
I. Feldspar:
- It has hardness of 6 on Mohs Scale.
- Silicon and oxygen in all types of feldspar.
- Sodium , potassium, calcium, and aluminium are found in specific feldspar variety.
- Half of Earth’s crust is composed of Feldspar.
- It has a light cream to salmon pink colour.
- Uses: It is used in ceramics and glass-making.
II. Quartz:
- It is a component of granite and sand with hardness level of 7 on Mohs scale.
- Silica is the constituent of quartz.
- Hard mineral, and virtually insoluble in water.
- It is white or colourless.
- Uses: in radio and radar industry.
III. Pyroxene:
- It consistes of calcium, aluminium, magnesium, iron and silica.
- 10% of earth’s crust is formed by pyroxene.
- It is green or black in colour.
- Commonly found in meteorites.
IV. Amphibole:
- Alumium, calcium, silica, iron, magnesium are major constituents of amphibole.
- 7% of earth’s crust is formed by these.
- It is green or black in colour.
- Another form of Amphibole is Hornblende.
- Uses: particularly in Asbestos industry.
V. Mica:
- Potassium, aluminium, magnesium, iron, silica are main constituents.
- 4% of Earth’s crust is formed of mica.
- Mica is generally found in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
- Uses: in electrical instruments.
VI. Olivine:
- Magnesium, iron, and silica are major elements of olivine.
- It has greenish crystals.
- Basically found in baslatic rocks.
- Uses: in jewellery.
Besides these main minerals, chlorite, calcite, magnetite, haematite, bauxite, and barite are also present in rocks.
Metallic Minerals
These contain metal content. It has three types:
- Precious metals – gold, silver, platinum, etc.
- Ferrous metals – iron and other metals often mixed with iron to form various kinds of steel.
- Non ferrous metals – includes metals like copper, lead, zinc, tin, aluminium.
Non Metallic Minerals
- These do not contain metal content.
- Sulphur, phosphates, and nitrates, etc.
- Uses: Cement is a mixture of non-metallic minerals.