For individuals familiar with banking industry, PSL/PSA are a thing to keep in mind all the time. For others, let us try and explain that here. As we all know that, the Banking sector in India is completely regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
<< Read about the role and functions of RBI here >>
RBI has very strict directives to all banks, including the Regional Rural Banks, to follow the minimum prescribed limit of giving loans to the priority sector on compulsory basis. The priority sector norms set by RBI are to be adhered by all the banks.
Such a initiative by the RBI was essential because, certain areas of Indian economy were getting neglected by these banks. As we all know that the banks are the lifeline of an economy, they perform various functions like lending facilities, taking deposits, mobilizing funds for businesses and aid in economic development.
Economic development cannot be for any one sector, it will benefit the country only when the development occurs across all strata of the society. This includes the poor, agricultural laborers, artisans, small entrepreneurs on one hand, and large businesses, corporates, companies, on the other hand.
Thus, the concept of priority sector was envisioned to ensure proper credit supply to otherwise ignored projects by the banks. Let’s look into various aspects of priority sector lending now:
I. The History of Priority Sector Lending:
- Priority sector came into much attention in 1972, following the National Credit Council’s plea that more emphasis should be given by commercial banks to the priority sector.
- Therefore, initially, in 1974, the commercial banks were given a target of 33.33 % of their total credit should go to the priority sector.
- Following the recommendations of Dr. K S Krishanaswamy Committee, this target was revised to 40% of the total credit given by the banks.
- The latest revision in PSL targets has been made by the M.V. Nair Committee in 2012.
II. What exactly is Priority Sector?
Dr. K S Krishnaswamy Committee defined priority sector as the sectors of economy involving Agriculture Finance, Retail Trade, Small Enterprises, Education Loans, Micro Credit and housing loans.
The Reserve Bank of India, describes Priority sector lending norms to include the following areas:
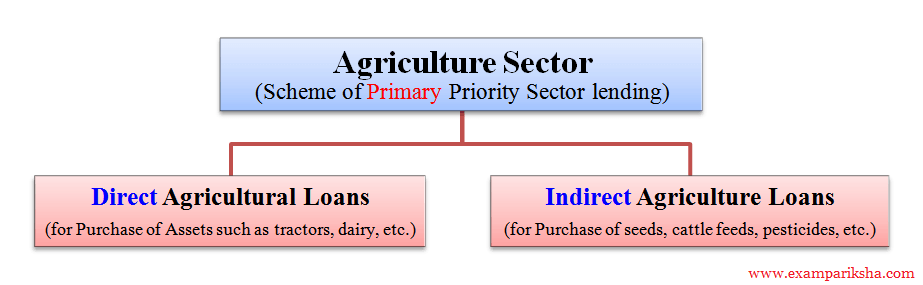
- Agriculture including Direct and Indirect Finance. Direct finance means loans and advances given to individual farmers, cooperative firms directly, small and marginal farmers. Indirect finance includes loans given to agricultural credit societies, large sized adivasi multi-purpose societies and farmers service societies.
- Small scale industries, this includes loans for setting up of industrial estates also.
- Small road and water transport operators with a limit for owning upto 10 vehicles.
- Small business, where the cost of equipment used for business does not to exceed 20 lakh rupees.
- Retail trade, with loans upto rupees 10 lakh.
- Professional and self-employed persons, with the borrowing limit upto 10 lakh rupees, with many terms and conditions.
- State sponsored organizations for upliftment of Scheduled Castes/Scheduled Tribes
- Education sector, includes educational loans to individuals.
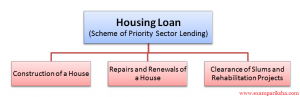
- Housing includes both direct and indirect loans with different limits set for rural and urban areas.
- Consumption loans covered under Consumption Credit scheme being run for weaker sections.
- Micro-credit to self help groups(SHGs) or Non Governmental Organizations (NGOs).
- Loans to the software industry upto Rs 1 crore rupees.
- Loans to the specified industries operating in the Food and Agro-processing sector, which have an investment in plant and machinery not exceeding Rs 5 crore.
- Loans to sanitation, health care and drinking water facilities and renewable energy. (newly added)
- Bank Investment in venture capital funds or companies that are registered with SEBI.
The Reserve Bank keeps on revising and updating these targeted values for priority sector lending according to the requirements of the economy.
Minimum Limits for Priority Sector Lending
The minimum limits are prescribed by RBI according to the ownership pattern of banks. For all local banks in both public and private sectors are required to lend 40% of their net bank credit (NBC), to the priority sector. For foreign banks the minimum limit is 32% of their NBC (Net Banking Credit) to the priority sector.
Specific Targets within the Priority Sector
The Domestic banks are required to lend 18% of the (Adjusted Net Banking Credit) ANBC to the agriculture sector and 10% of the Net Banking Credit has to go to the weaker section. The RBI has recommended a sub-target of 8% of the ANBC for small and marginal farmers, that is to be achieved in a phased manner. However, the foreign banks are required to lend 10% of their NBC to the small-scale industries and 12% of their NBC for export credit.
The rate of interest on different priority sector loans will be according to RBI’s directives issued from time to time, which is basically linked to Base Rate of banks at present. It is interesting to note that Priority sector guidelines do not lay down any preferential rate of interest for priority sector loans.