The period between the 1st century B.C. to the end of 2nd century A.D. in Southern India is known as Sangam Period. It has been named after the Sangam academies during that period.
According to the Tamil legends, there were three Sangams (Academy of Tamil poets) held in the ancient South India popularly called Muchchangam. These Sangams flourished under the royal patronage of the Pandya kings of Madurai.
- The First Sangam, is believed to be held at Madurai, attended by gods and legendary sages. No literary work of this Sangam is available.
- The Second Sangam was held at Kapadapuram, only Tolkappiyam survives from this.
- The Third Sangam at Madurai was founded by Mudathirumaran. A few of these Tamil literary works have survived and are a useful sources to reconstruct the history of the Sangam period.
Sangam Literature:
The Sangam literature includes Tolkappiyam, Ettutogai, Pattuppattu, Pathinenkilkanakku, and two epics named – Silappathigaram and Manimegalai .
- Tolkappiyam was authored by Tolkappiyar, it is considered the earliest of Tamil literary work. Though it is a work on Tamil grammar but it also provides insights on the political and socio-economic conditions of the time.
- Ettutogai (Eight Anthologies) consist of eight works – Aingurunooru, Narrinai, Aganaooru, Purananooru, Kuruntogai, Kalittogai, Paripadal and Padirruppattu.
- The Pattuppattu (Ten Idylls) consist of ten works – Thirumurugarruppadai, Porunararruppadai, Sirupanarruppadai, Perumpanarruppadai, Mullaippattu, Nedunalvadai, Maduraikkanji, Kurinjippatttu, Pattinappalai and Malaipadukadam .
- Pathinenkilkanakku contains eighteen works about ethics and morals. The most important among these works is Tirukkural authored by Thiruvalluvar, the tamil great poet and philosopher.

Thiruvalluvar Statue at Kanyakumari
- The two epics Silappathigaram is written by Elango Adigal and Manimegalai by Sittalai Sattanar. They also provide valuable details about the Sangam society and polity.
Other Sources that give details about the Sangam Period are –
- the Greek authors like Megasthenes, Strabo, Pliny and Ptolemy mentioning about commercial trade contacts between the West and South India.
- Also, the Ashokan inscriptions mention about the Chera, Chola and Pandya rulers to the south of Mauryan empire.
- Another inscription, Hathikumbha inscription of Kharavela of Kalinga also has mention of Tamil kingdoms.
Political History of Sangam Period:
Cheras:
The Cheras had their rule over major parts of modern Kerala/ malabar areas.
- The capital of Cheras was Vanji and their important seaports were Tondi and Musiri.
- They had the palmyra flowers as their garland.
- The insignia of Cheras is the” bow and arrow”.
- The Pugalur inscription of the 1st century AD has reference to three generations of Chera rulers.
- The important ruler of Cheras was Senguttuvan who belonged to 2nd century A.D.
- His military achievements have been chronicled in epic Silapathikaram, with details about his expedition to the Himalayas where he defeated many north Indian rulers.
- Senguttuvan introduced the Pattini cult or the worship of Kannagi as the ideal wife in Tamil Nadu.
- He was the first to send embassy to China from South India.
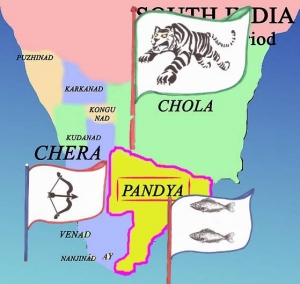
Cholas:
The Chola kingdom in the Sangam period extended from Northern Tamil Nadu to southern Andhra Pradesh.
- Their capital was firstly at Uraiyur and later shifted to Puhar(Tanjore).
- King Karikala was a famous king of the Sangam Cholas.
- The insignia of Cholas was “tiger”.
- Pattinappalai portrays his life and military conquests.
- Many Sangam Poems mention the Battle of Venni where he defeated the confederacy of Cheras, Pandyas and eleven minor chieftains.
- He also fought at Vahaipparandalai in which nine enemy chieftains submitted before him.
- Hence, Karikala’s military achievements made him the overlord of the whole Tamil country.
- Therefore, Trade and commerce flourished during his reign.
- He also built irrigation tanks near river Kaveri to provide water for reclaimed land from forest for cultivation.
Pandyas:
The Pandyas ruled over the present day southern Tamil Nadu.
- Their capital was Madurai.
- Their insignia was the “carp”.
- King Neduncheliyans also known as Aryappadai Kadantha Neduncheliyan. He ordered the execution of Kovalan. The curse of Kovalan’s wife-Kannagi burnt and destroyed Madurai.
- Maduraikkanji was written by Mangudi Maruthanar which describes the socio-economic condition of the flourishing seaport of Korkai.
Sangam Polity and administration:
During the Sangam period hereditary monarchy was the form of government. Each of the dynasties of Sangam age had a royal emblem – tiger for the Cholas, carp for the Pandyas, and bow for the Cheras.
- The king was assisted by a wide body of officials who were categorised into five councils.
- They were ministers (amaichar), priests (anthanar), envoys (thuthar), military commanders (senapathi), and spies (orrar).
- The military administration was efficiently organized with each ruler a regular army was associated.
- The chief source of state’s income was Land revenue while a custom duty was also imposed on foreign trade.
- Major source of fulfilling the royal treasury was the booty captured in wars.
- The roads and highways were maintained and guarded to prevent robbery and smuggling.
Position of Women during Sangam Age:
A lot of information is available in the Sangam literature to understand the position of women during the Sangam age.
- There were women poets like Avvaiyar, Nachchellaiyar, and Kakkaipadiniyar who flourished and contributed to Tamil literature.
- Love marriage was a common practice and women were allowed to choose their life partners.
- But, life of widows was miserable.
- There is also a mention about the practice of Sati being prevalent in the higher strata of society.
Economy of the Sangam Age:
- Agriculture was the chief occupation where rice was the most common crop.
- The handicraft included weaving, metal works and carpentry, ship building and making of ornaments using beads, stones and ivory.
- These were in great demand of all above products in the internal and external trade as this was at its peak during the Sangam period.
- A high expertise was attained in spinning and weaving of cotton and silk clothes. Various poems mention of cotton clothes as thin as a cloud of steam or like a slough of snake. These were in great demand in the western world especially for the cotton clothes woven at Uraiyur.
- The port city of Puhar became an important place of foreign trade, as big ships entered this port containing precious goods.
- Other significant ports of commercial activity were Tondi, Musiri, Korkai, Arikkamedu and Marakkanam.
- Many gold and silver coins that were issued by the Roman Emperors like Augustus, Tiberius and Nero have been found in all parts of Tamil Nadu indicating flourishing trade.
- Major exports of the Sangam age were cotton fabrics and spices like pepper, ginger, cardamom, cinnamon and turmeric along with ivory products, pearls and precious stones.
- Major imports for the traders were horses, gold, and sweet wine.