Agricultural seasons of India are three chief ones – Kharif, Rabi and Zaid.
Kharif Crop:
These are the crops which are sown at the beginning of the south-west monsoon season (June to July) and are harvested at the end of the same season (September and October). Major crops grown in this season include rice, jowar, bajra, groundnut, jute, cotton, seasmum, some pulses like moong, urad, etc.
Rabi Crops:
These are crops sown at the beginning of the cold season (October to December) and are harvested at the beginning of the warm season (March to April). They include wheat, gram, barley, potatoes, jowar, oil seeds such as linseed, rapeseed and mustard.
Zaid Kharif Crops:
These are sown in August and September. And are harvested in months of December and January. Most of the oil seeds such as mustard and tori are grown in this season.
Zaid Rabi Crops:
These crops are sown at the beginning of the hot season in February and March and are harvested in the months of April and May. Summer vegetables and fodder crops like jowar, maize, water melons, cucumbers, etc. are important among these Zaid rabi crops.
Food Crops of India
Rice:
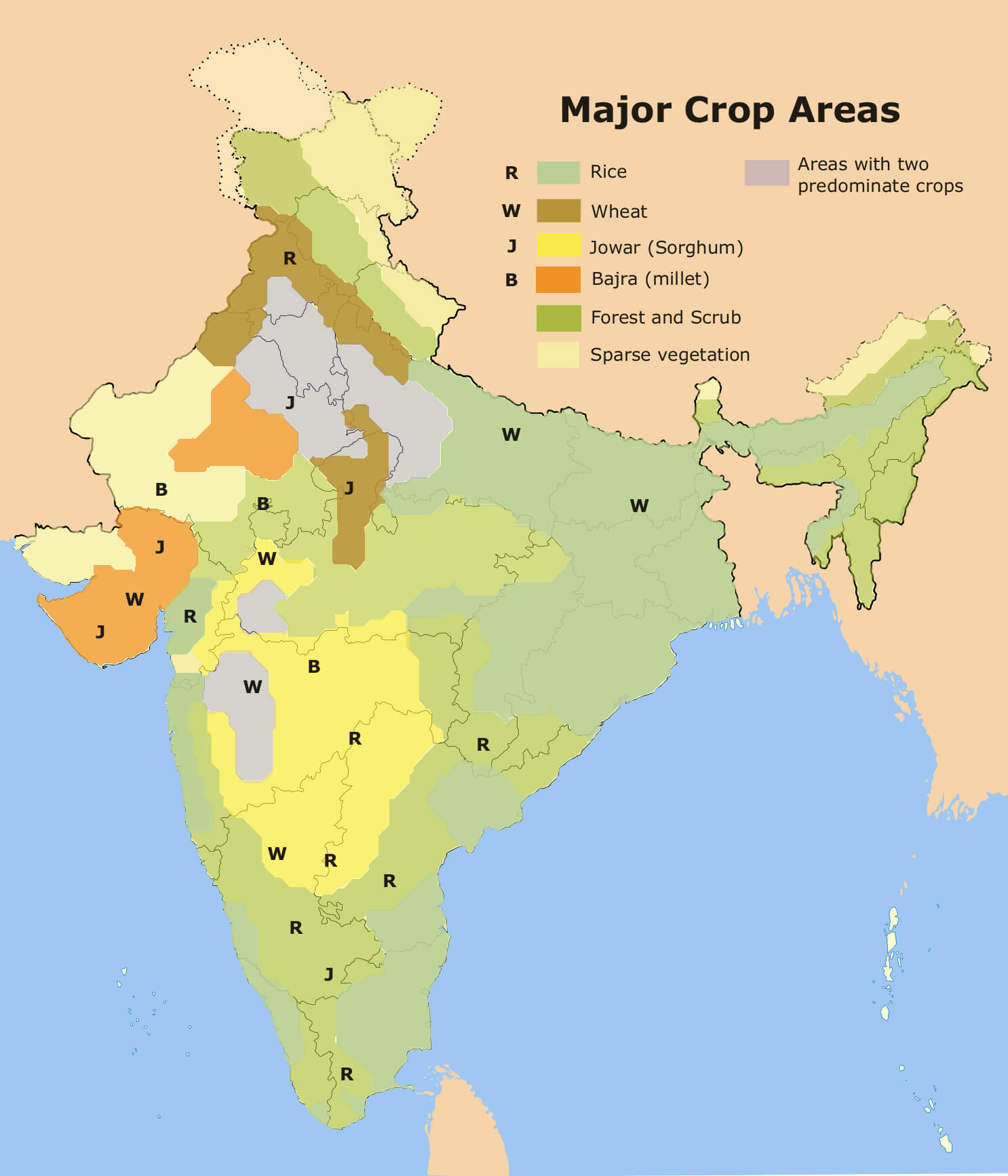
It requires early growing stage 16-20 degree celcius and at ripening stage, temperature of 18-32 degrees Celcius. Rainfall is required in range of 150-300 cm, described as heavy rainfall. Rice is grown extensively in Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Assam and Maharashtra.
Wheat:
It grows best when it receives temperature in range of 10-15 degree celcius and ripening stage temperature of 25-28 degrees celcius. Rainfall is required in the range of 50-100 cm. The area and state where wheat is grown are Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana.
Maize:
The temperature range required 21-27 degrees celcius cannnot stand frost at any stage of its development. The rainfall required is 50-100 cm along with sunshine which promotes growth. While cold and dry conditions are required at the ripening stage. it is grown in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Rajsthan and punjab.
Millets- Jowar, Bajra, Ragi:
They require temperature 27-32 degrees celcius and survive high temperatures and drought conditions. The rainfall required is 50-120 cm, that is why it is known as dry crop does not require much rain. Jowar and Bajra grown in Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajsthan. Ragi is grown in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh.
Pulses:
The temperature required is 20-30 degrees Celsius. The rainfall required is 50-75 cm. It is grown all over India.
Important Cash Crops of India
Sugarcane:
The temperature required is in range of 20-30 degree Celcius. The rainfall is required in range of 75-150 cm, where plenty of water is required in the growing stage. Sugarcane is a cash crop grown in Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Bihar, Haryana and Punjab.
Cotton:
The temperature required is between 21-27 degrees celcius. The rainfall required is 50-80 cm of well distributed rain. It is grown in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, Andhra Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka and Rajasthan produce long staple cotton.
Jute:
It requires temperature of 27-34 degrees Celsius. The rainfall required is 170-200 cms. It is chiefly grown in West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, Assam.
Tobacco:
It requires temperature of 20-40 degrees celcius and rainfall of 75-100 cms. Majority of tobacco is grown in Andhra Pradesh(about 90%), then in Karnataka, Maharashtra, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Orissa and Rajsthan.