Price Indices in India – An Overview
There are three major indices used in India for comprehensive assessment of prices and production.
(WPI) Wholesale Price Index in India
- In India, the Wholesale price index (WPI) is the main measure of inflation. The WPI measures the price of a representative basket of wholesale goods. WPI captures price movements in a most comprehensive way. It is widely used by Governments, banks, industry and business circles.
- Important monetary and fiscal policy changes are linked to WPI movements.It is in use since 1939 and is being published since 1947 regularly.
- It is calculated by – Office of the Economic Adviser <In DIPP (Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion) < In Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- It is released on three duration basis. A) Weekly: on Every Thursday for Primary Articles and Fuel Group. B) Monthly : On 14th of Every month for all commodities. C) Final:Final list is released every two months (~EIGHT weeks). When they get authentic price data for all commodities.
- Wholesale price index is divided into three groups: Primary Articles (20.1 percent of total weight), Fuel and Power (14.9 percent) and Manufactured Products (65 percent). Food Articles from the Primary Articles Group account for 14.3 percent of the total weight. The most important components of the Manufactured Products Group are Chemicals and Chemical products (12 percent of the total weight); Basic Metals, Alloys and Metal Products (10.8 percent); Machinery and Machine Tools (8.9 percent); Textiles (7.3 percent) and Transport, Equipment and Parts (5.2 percent).
- The current WPI has a basket of 676 items.
- Problem with WPI: The major issue with this index is that ‘the general public does not buy at the wholesale’. Thus WPI does not give real picture of the amount of pressure of increasing prices on the general public. However, the increase in wholesale prices does affect the retail prices and as such give some indication of the consumer prices.
- Headline WPI: calculated using above all three groups. primary, fuel and power, manufactured products.
- Core WPI: calculated using non-food manufactured products. Core WPI = Headline WPI – (primary + fuel + food mfg. industries)
- It is calculated using Laspeyres formula for weighted arithmetic mean.Currently , Base year 2004.
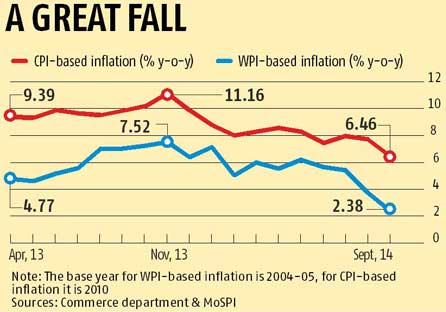
WPI and CPI inflation in India
- The Wholesale Price Index focuses on the price of goods traded between corporations, rather than goods bought by consumers, which is measured by the Consumer Price Index. The purpose of the WPI is to monitor price movements that reflect supply and demand in industry, manufacturing and construction. This helps in analyzing both macroeconomic and microeconomic conditions of an economy.
Index of Industrial Production (IIP) in India
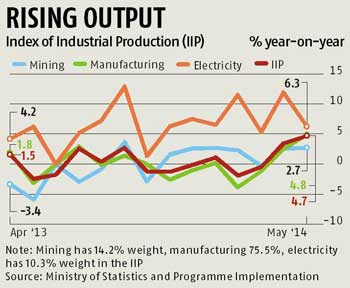
IIP in India
- Index of Industrial Production (IIP) measures the quantum of changes in the industrial production in an economy and captures the general level of industrial activity in the country. It is a composite indicator expressed in terms of an index number which measures the short term changes in the volume of production of a basket of industrial products during a given period with respect to the base period(2004).
- The base year is always given a value of 100. The current base year for the IIP series in India is 2004-05. So, if the current IIP reads as 116 it means that there has been 16% growth compared to the base year.
- It is calculated by Central Statistics Office (CSO) < In the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI)
- It is brought out on monthly basis with the time lag of six weeks from the reference month (on 12th of the Month, or if 12th is a Gazetted Holiday, on the previous working day).Although IIP is just a short term indicator. The actual results come with the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI).
- Uses of IIP: The IIP measures volume changes in the production of an economy
Provides a measurement that is free of influences of price changes
Data used in Government policy planning purposes, Industrial Associations, Research Institutes and Academicians. - Industrial Production in the IIP comprises three distinct groups of industry, (a) Mining, (b) Manufacturing and (c) Electricity.
- Core IIP: to provide an indication of how the industries whose production performance was ‘core’ in nature because of their likely impact on general economic activity as well as other industrial activity, with six industries, viz. Coal, Cement, Electricity, Crude Oil, Refinery products, and Steel. When the base year for IIP was revised to 2004-05, the base year for the Index of Core Industries was also revised to 2004.
- The Eight Core Industries are Coal, fertilizer, electricity, crude oil, natural gas, refinery products, steel, and cement, which have count in IIP.
- The data for compilation of IIP is received from 16 different source agencies viz. Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP); Indian Bureau of Mines; Central Electricity Authority; Joint Plant Committee; Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas; Office of Textile Commissioner; Department of Chemicals & Petrochemicals; Directorate of Sugar; Department of Fertilizers; Directorate of Vanaspati, Vegetable Oils & Fats; Tea Board; Office of Jute Commissioner; Office of Coal Controller; Railway Board; Office of Salt Commissioner and Coffee Board.
- IIP covers 682 items comprising Mining (61 items), Manufacturing (620 items) & Electricity (1 item). The weights of the three sectors are 14.16%, 75.53% and 10.32% respectively and are on the basis of their share of GDP at factor cost during 2004-05. The general scope of IIP, as recommended by United Nations Statistics Division includes Mining & Quarrying, Manufacturing, Electricity, Gas steam, Air conditioning supply, Water supply, Sewerage, Waste management and Remediation activities. But in India, due to constraints of data availability and other resources, the index is compiled using figures of mining, manufacturing and electricity sectors only.
<< Click here to read the rules for Prepositions in English>>
(CPI) Consumer Price Index in India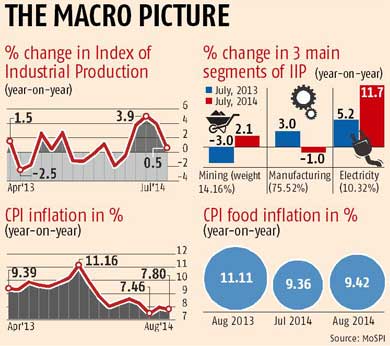
- CPI is a measure of change in retail prices of goods and services consumed by defined population group in a given area with reference to a base year.The consumer price index number measures changes only in one of the factors- prices.
- This basket of goods and services represents the level of living or the utility derived by the consumers at given levels of their income, prices and tastes. This index is an important economic indicator and is widely considered as a barometer of inflation, a tool for monitoring price stability and as a deflator in national accounts.
- Consumer price index is used as a measure of inflation in around 157 countries. The dearness allowance of Government employees and wage contracts between labour and employer is based on this index. The formula for calculating Consumer Price Index is Laspeyre’s with base year 2010.
- It is calculated by Central Statistics Office (CSO) < In the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI)
- It is brought out on monthly basis for urban, rural and all India.Also Annually: with lag of one month.And State/UT’s separate Consumer Price Index are also released if they provide 80% of the required data.
- The origin of Consumer Price Index can be traced to the period after first world war when there was a sharp rise in prices and cost of living. The erosion in the real wages of the workers led to a demand by the workers for compensation.
- Presently the consumer price indices compiled in India are CPI for Industrial workers CPI(IW), CPI for Agricultural Labourers CPI(AL) & Rural Labourers CPI(RL) and CPI ( Urban) and CPI(Rural). Consumer Price Index for Urban Non Manual Employees was earlier computed by Central Statistical Organisation. However this index has been discontinued since April 2008.
- The CPI(IW) and CPI(AL& RL) compiled are occupation specific and centre specific and are compiled by Labour Bureau. This means that these index numbers measure changes in the retail price of the basket of goods and services consumed by the specific occupational groups in the specific centres.
- CPI(Urban) and CPI(Rural) are new indices in the group of Consumer price index and has a wider coverage of population. This index compiled by Central Statistical Organisation tries to encompass the entire population and is likely to replace all the other indices presently compiled.
- The index is a measure of the average price which consumers spend on a market-based “basket” of goods and services. Inflation based upon the consumer price index (CPI) is the main inflation indicator in most countries. Based on the recommendations of Urjit R. Patel Committee report that have been implemented by RBI, a new CPI (combined) as the key measure of inflation.
<<Click here for Powers of Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha in Indian Parliament>>





