Various Types of Banks and Their Functions – Banking Study Material & Notes
Broadly, banks are classified either into commercial banks or as central bank. they are also classified as Scheduled and Non-scheduled Banks.
Scheduled banks have been included in the second schedule of the Reserve Bank, and fulfils the following three criteria:
- It must have a paid up capital of at least Rs. 5 lakhs.
- It must fulfil the RBI norms about no activity that may be detrimental to the depositors interests.
- It must be a Corporation(not a partnership or a single ownership firm).
Non-Scheduled Banks are excluded from the Second schedule of RBI. The Reserve Bank does not exercise much control over them, but they report monthly to RBI.
Now, We shall first look into Central Bank first. The central bank has the primary function of regulating commercial banks and other economic activities in the economy. It acts as a Banker’s Bank. In India, the central Bank is the Reserve Bank of India. It is the apex bank who controls all other banks by regulating and supervising their activities.
<< Read about the functions and role of RBI in detail here >>
Now, lets talk about Commercial banks. These are those banks which provide banking services to people with a profit motive. They charge a certain prescribed amount for the services they provide.
There are several types of commercial banks functioning in India based upon different categories:
I. Public Sector Banks – Majority stake is held by Government
- State Bank of India and its associate banks: These associate banks are State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Mysore, State Bank of Patiala, and State Bank of Travancore.
- Nationalised Banks– These are those commercial banks that have been nationalized for fulfilling the social objectives of the government. There are 20 Nationalised banks in India. These are – Allahabad Bank, Andhra Bank, Bank of Maharashtra, Bank of Baroda, Canara Bank, Central Bank of India, Bank of India, , Corporation Bank, Dena Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, IDBI Bank Ltd., Oriental Bank of Commerce, Indian Bank, Punjab & Sind Bank, Punjab National Bank, Union Bank of India, Syndicate Bank, United Bank of India,UCO Bank, and Vijaya Bank.
- Regional Rural Banks(RRB)– These banks have been established to strengthen the rural economy. They facilitate the credit and deposit flow for farmers, artisans, labourers in their limited local area. These banks are jointly owned by the central and state government along with a sponsor commercial bank.
<< Read more about RRB here >>
II. Private Sector Banks – Majority share capital is with private individuals & corporates
- Old Private Banks – There are fourteen old private banks operating in India. These banks were not nationalised when other banks were nationalised in 1969 and 1980. These are- Catholic Syrian Bank Ltd., Dhanalakshmi Bank Ltd., City Union Bank Ltd., Federal Bank Ltd., Lakshmi Vilas Bank Ltd., ING Vysya Bank Ltd., Karur Vysya Bank Ltd., Karnataka Bank Ltd., , Nainital Bank Ltd., Ratnakar Bank Ltd., Jammu & Kashmir Bank Ltd., South Indian Bank Ltd., SBI Commercial & International Bank Ltd, and Tamilnad Mercantile Bank Ltd.
- New Private Banks- There are seven new private banks functioning in the Indian economy. These are- Axis Bank Ltd., Development Credit Bank Ltd, ICICI Bank Ltd., IndusInd Bank Ltd., Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd., HDFC Bank Ltd., and Yes Bank Ltd.
- Foreign Banks- These banks have their registered head offices in a foreign country, while they operate their branches in India. They can operate in India either through wholly-owned subsidiaries or through branches. There are 32 foreign banks operating their various branches in India.
- Co-operative Banks – Cooperative banks are those scheduled banks that are regulated by RBI, under a cooperative structure to provide credit to all actegories of businesses. Their ownership structure is unique where like minded individuals and companies pool in money together to support credit facilities to businesses. These can operate in either Urban or Rural setting. That is another criteria to differentiate these co-operative banks.
- The types of banks in India can be understood from the following table, which explains what kind of customer base different types of banks have.
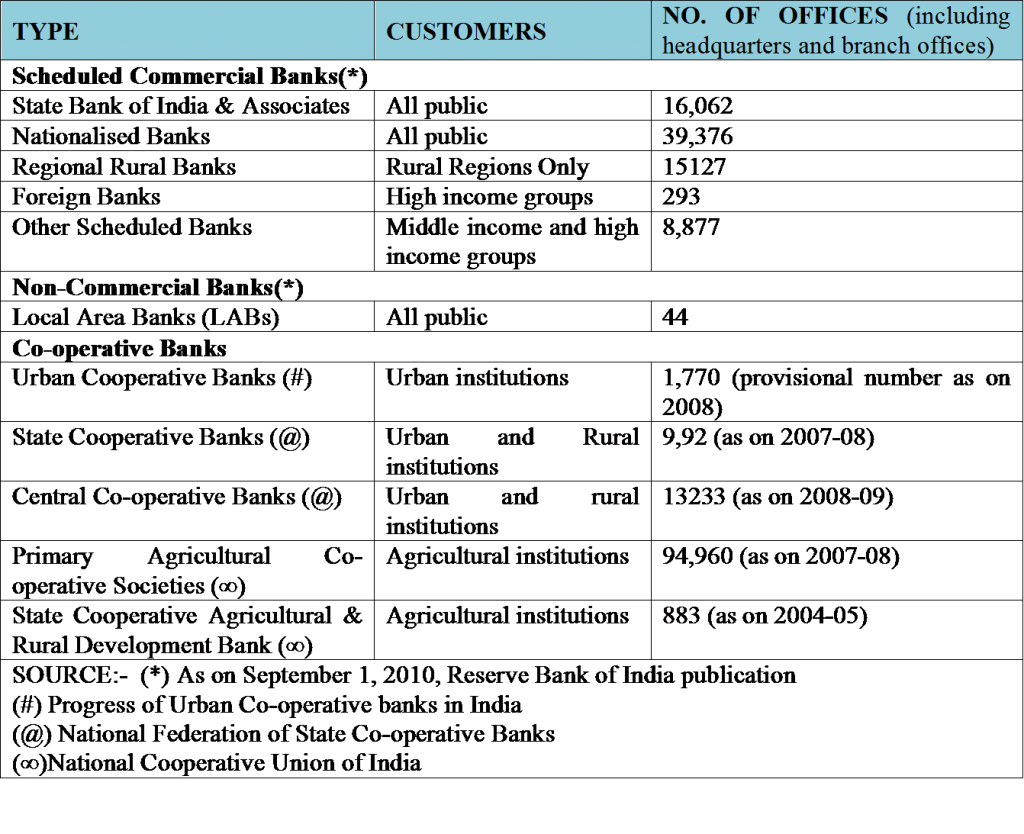
This classification of various types of banks in India is highly useful for solving the banking awareness questions asked in exams conducted by IBPS, SBI, RBI, and other recruiters in the banking industry. This knowledge also helps in facing interviews confidently. As an aspirant for banking exams, one must have updated knowledge of these classifications about the types of banks. Therefore, we have compiled this short quick revision notes for students.
We hope this concise material is helpful in revision. Please feel free to let us know if there is anything that you want us to add in this article. Tell us your opinion in the comments below.