India has a monsoon kind of climate. The whole country has a tropical monsoonal climate since, the greater part of the country lies within tropics. And the climate is influenced by the south-west and North-east monsoons.
The position of the mountain ranges and direction of the rain bearing winds are the two main factors that determine the climate of India. Alternating season is the chief characteristic feature of Indian Climate.
The climate is about the average weather conditions, which have been measured over many years.
The climate of India has broadly been described as monsoon type. Due to India’s location in the tropical region most of the rain is brought by monsoon winds.
India’s place called as Mawsynram in Meghalaya receives the world’s highest rainfall. While in a particular year it might not rain at all in Jaisalmer in Rajasthan.
Broadly, the major seasons recognized in India by the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) are:
- Cold weather season known as Winter from December to February. Average temperature around 10-15 degree celcius in the Northwest. Temperatures rise towards equator, average around 20-25 degrees celcius in mainlaind India’s southeast.
- Hot weather season known as Summer from March to May. In western and southern regions, the month of April is hottest. For northern regions, month of May is hottest. Average temperature around 32-40 degrees celcius in major parts of the interior.
- South-West monsoon season known as rainy season from month of June to September. In this season humid southwest monsoon moves across the country causing rains.
- Season of retreating monsoon known as Autumn in months of October and November. in northwestern India, months of October and November are generally cloudless.
Traditionally, India has six seasons with each being two months long in duration. They are based on the astronomical division of 12 months into 6 parts. These seasons are reflected in the ancient Hindu calender. These are listed with their traditional names below:
- Spring (Vasanta)
- Summer (Grishma)
- monsoon (Varsha)
- Early Autumn (Sarada)
- Late Autumn (Hemanta)
- Winter (Sisira)
Factors affecting the Climate of India
The Climate in India is affected by following factors
- Latitude
- Himalaya Mountains
- Altitude
- Distance from the sea
- Geographical limits like western disturbances, conditions in the regions surrounding India, Conditions over the ocean.
- Jet Streams.
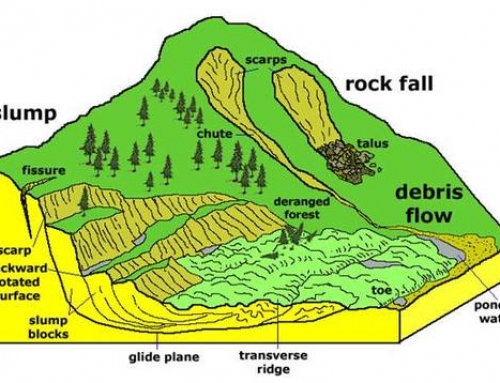
The Cold Weather Season
During the winter season, cool and dry winds blow from direction of North towards South.
During winter season, the Sun rays do not fall directly, they are slant, as a result, the temperatures are quite low in Northern India.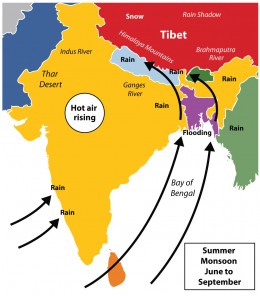
The Hot weather Season
In the Hot weather season, the Sun rays more or less directly fall in this region. Therefore temperature becomes very high. Hot and dry winds called loo blow during the day.
South-west Monsoon Season
This season is marked by the onset and advance of monsoon. The winds blow from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal towards the land. They carry moisture with them. When these winds strike the mountain barriers rainfall occurs.
Season of Retreating Monsoon
When winds move back from the mainland to the Bay of Bengal, this season is known by name of the retreating monsoons. The southern part of India, particularly Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh receive rainfall in this season.
<< Read about Priority Sector Lending here>>
El-Nino and the Indian Monsoon
El Niño is a complex weather pattern resulting from variations in ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific region along South America. The term El Niño refers to the large-scale ocean-atmosphere climate interaction linked to a periodic warming in sea surface temperatures across the central and east-central Equatorial Pacific.
The system involves oceanic and atmospheric phenomena with the appearance of warm currents off the coast of Peru in the eastern pacific and affects weather in many places including India. It is merely an extension of the warm equatorial current which gets replaced temporarily by cold Peruvian current or Humbolt Current.
This results in two things:
- The distortion of equatorial atmosphere circulation
- Irregularities in the evaporation of sea water.
- Reduction in the amount of Planktons which further reduces the amount of fish in the sea.
It is a complex weather system that appears once every three to seven years, bringing drought, floods and other weather extremes to different parts of the world.
<< Read about history of Rashtrakuta dynasty in India here>>
<< Click here to revise the list of National Park in India>>