The plant community left undisturbed over a long time to adjust themselves to climate and soil conditions – natural vegetation.
Types of forest:
- Tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen
- Tropical deciduous forests
- Tropical thorn Forest
- Montane Forest
- Littoral and Swamp Forest
Tropical Evergreen & Semi Evergreen Forest:
They are found in warm and humid areas, annual rainfall over over 200 cm, mean temperature is 22 degrees celcius
Western slope of western Ghats, hills of north east, Andaman & Nicobar islands. They are well stratified forest. The instance Rosewood, Mahogony, Aini, Ebony, etc.
Semi-evergreen Forest:
They are present in less rainy areas. The mixture of evergreen and moist deciduous trees which have under-growing climbers give evergreen character. They have White cedar, Hollock, Kail, etc.
Britishers replaced the oak forests in Garhwal, Kumaon with Pine(chirs) which was needed for railway lines.
Tropical Deciduous Forest/Natural Vegetation:
It is most widespread called Monsoon forest. It is It occurs in rainfall of 70-200 cm. There are two types of deciduous forest, moist and dry.
Moist Deciduous : Have rainfall 100-200 cm, found in NE states along Himalayas foothills, eastern slope of Western Ghats and Orissa. Teak, Sal, Shisham, Hurra, Mahua, Amla, Semul, Kussum and Sandalwood,etc.
Dry Deciduous : Rainfall 70-100 cm, in rainier part of Peninsula, UP plains and Bihar. In high rainfall, Parkland landscape (open, with trees). They shed leaves in dry season. Other trees are Tendu, Palas, Amaltas, Bel, Khair and Axlewood,etc.
Tropical Thorn Forest/Natural Vegetation:
It has rainfall less than 50 cm, semi-arid areas. Plants remain leafless, shrub vegetation. The trees of babool, ber, wild date palm, khair, neem, khejri, Palas, etc. Tussocky grass upto 2 cm height as undergrowth.
Montane Forest:
Montane forest has two types, Northern and Southern types.
Northern Montane Forest Vegetation:
Ranges from tropical to tundra with altitude. At the foothills, it is deciduous and wet temperate type of forest at 1000-2000m. Oak and Chestnut in West Bengal , Uttaranchal hills. At 1500-1750 m , there are pine forest, Chir pine commercial tree, deodar endemic specie on western Himalayas used in construction. Chinar and walnut in Kashmir.
At 2225-3048 m, Blue pine, spruce, temperate grasslands. At higher altitude there is alpine forest and pastures.
At 3000-4000 m, Silver firs, Juniper, pines, birch, Rhododendron. At higher reaches, moses and lichens like tundra are found. Pastures are used for transhumance by Gujjars, Bakarwals, Bhotiys, Gaddis.
Southern Montane Forest:
Western Ghats, Vindhya, Nilgiris in three areas. Closer to tropics, 1500 m high in temperate in highs and Sub-tropical in lows especially western Ghats in Kerala, TN, Karnataka.
Also in Satpura, Maikal ranges. Other trees – Magndia, Laurel, Cinchona, wattle.Sholas- temperate forest in Nilgiri, Anaimalai and Palani hills.
Littoral and Swamp Forest:
The natural vegetation of littoral and swamp type is 70% wetland under paddy. Total 3.9 million hectare wetlands. Two protected water-fowl habitats under (Ramsar convention) and the convention of wetlands of International importance(among UN members).
Eight categories of wetlands in India:
- Reservoirs of Deccan plateau in south along with lagoons and other wetlands of Southern West Coast .
- Saline Saline expanses of Rajasthan, Gujarat and Gulf of Kachchh.
- Freshwater lakes and reservoirs from Gujarat through Rajasthan and MP.
- Delta wetlands and lagoons of East coast (Chilaka lake).
- Freshwater marshes of Gangetic plain.
- Floodplains of Brahmaputra, marshes and swamps in hills of northeast India and Himalayan foothills.
- Lakes and rivers of Montane region of Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Mangrove forest and other wetlands of Andaman and Nicobar island arcs.
Mangroves:
They grow in salt marshes, tidal creeks, mud flats and estuaries. There are salt tolerant plant species. They provide shelter for various species of birds. India has world’s 7% of mangrove forest. Andaman & Nicobar islands, Sunderbans of West Bengal are highly developed.
They are also found in Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna deltas.
Forest cover:
Forest area is the notified area as forest land irrespective of existence of trees. 23.28% based on slate revenue department records. Actual forest cover is the area occupied by forest with canopy, 20.55% based on aerial photographs and Satellite imageries.
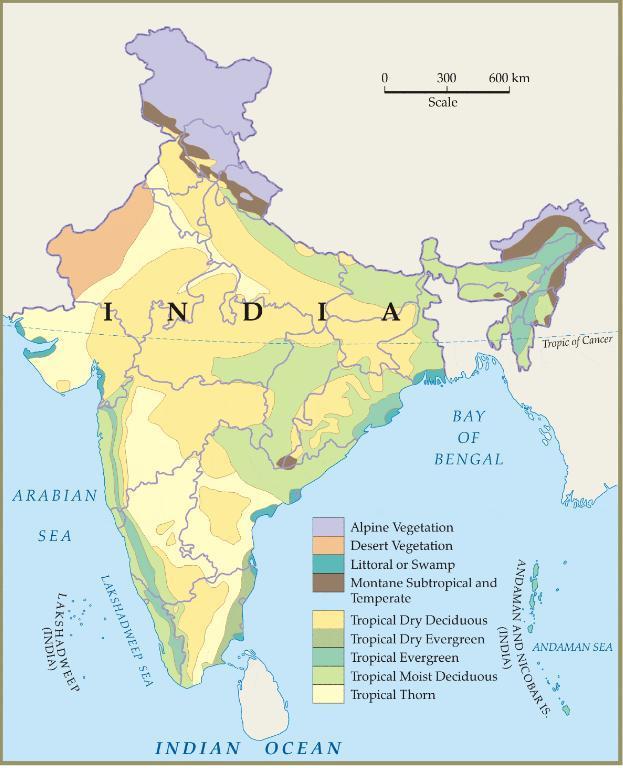
Types of Natural Vegetation in India
Lakshadweep has 0% forest area.
<< Read about Post Mauryan Period in Ancient Indian History here>>
Forest Conservation:
Forest have intricate interrelationship with life & Environment. The natural vegetation has numerous direct and indirect advantages to economy and society.
Forest Policy, 1988, emphasize sustainable forest management to conserve and expand forest reserve and to meet local needs of people.
Aims of Forest and Natural Vegetation Conservation:
- 33% area under forest cover.
- Maintaining environment stability and restore forests where ecological balance was disturbed.
- Conserving natural heritage of the country, biological diversity and genetic pool.
- Check soil erosion, extension of desert lands and reduction of floods and droughts.
- Increasing forest cover through social forestry and afforestation on degraded land.
- Increasing productivity of forest to make timber, fuel, fodder and food available to rural population dependent on forests and encourage substitution of wood.
- Creating massive movement involving women to encourage planting, stop felling of trees and thus, reduce pressure on existing forest.
<< Read about list of Council of Ministers in Union cabinet here>>
<< Click here to know about Forward Market Commission’s role in Indian Economy>>